EEG and tACS electrode montages and tACS current simulation results. A
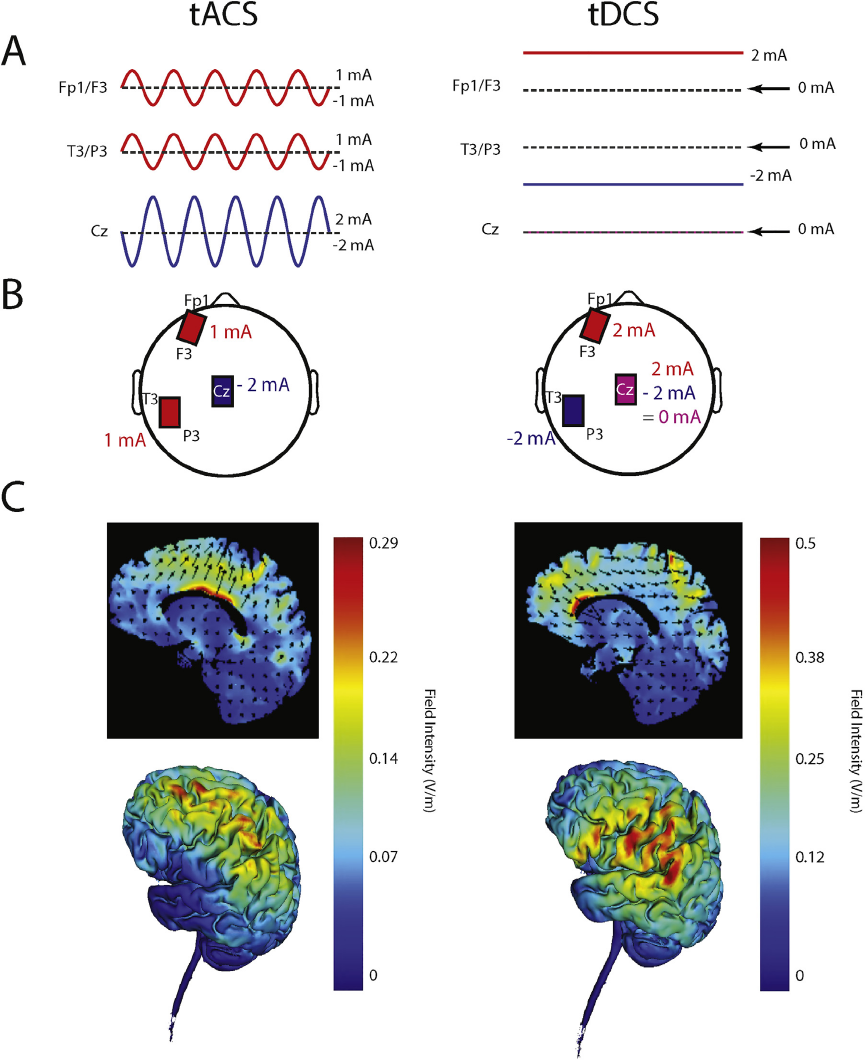
Download scientific diagram | EEG and tACS electrode montages and tACS current simulation results. A tACS ring electrode was centered position P3 of the international 10-20 system. EEG electrodes were positioned on P03, P04, Fz (ground) and both mastoids (references). tACS current simulations as created in SimNIBS show the norm of the electric field in V/m on an example brain, from three different viewpoints. from publication: “Broadband Alpha Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation”: Exploring a new biologically calibrated brain stimulation protocol | Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) can be used to study causal contributions of oscillatory brain mechanisms to cognition and behavior. For instance, individual alpha frequency (IAF) tACS was reported to enhance alpha power and impact visuospatial attention | Alpha, Transcranial direct current stimulation and Brain Stimulation | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Transcranial alternating current stimulation induces long-term augmentation of neural connectivity and sustained anxiety reduction

Montage matters: the influence of transcranial alternating current stimulation on human physiological tremor. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Procedure and tACS electrode montage. (A) Left: Alternating

Probing EEG activity in the targeted cortex after focal transcranial electrical stimulation - ScienceDirect

Common tDCS/tACS montages and corresponding simulated electric field

Transcranial Electrical Stimulation: Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS), Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS), Transcranial Pulsed Current Stimulation (tPCS), and Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation (tRNS)
Directionality of the injected current targeting the P20/N20 source determines the efficacy of 140 Hz transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS)-induced aftereffects in the somatosensory cortex
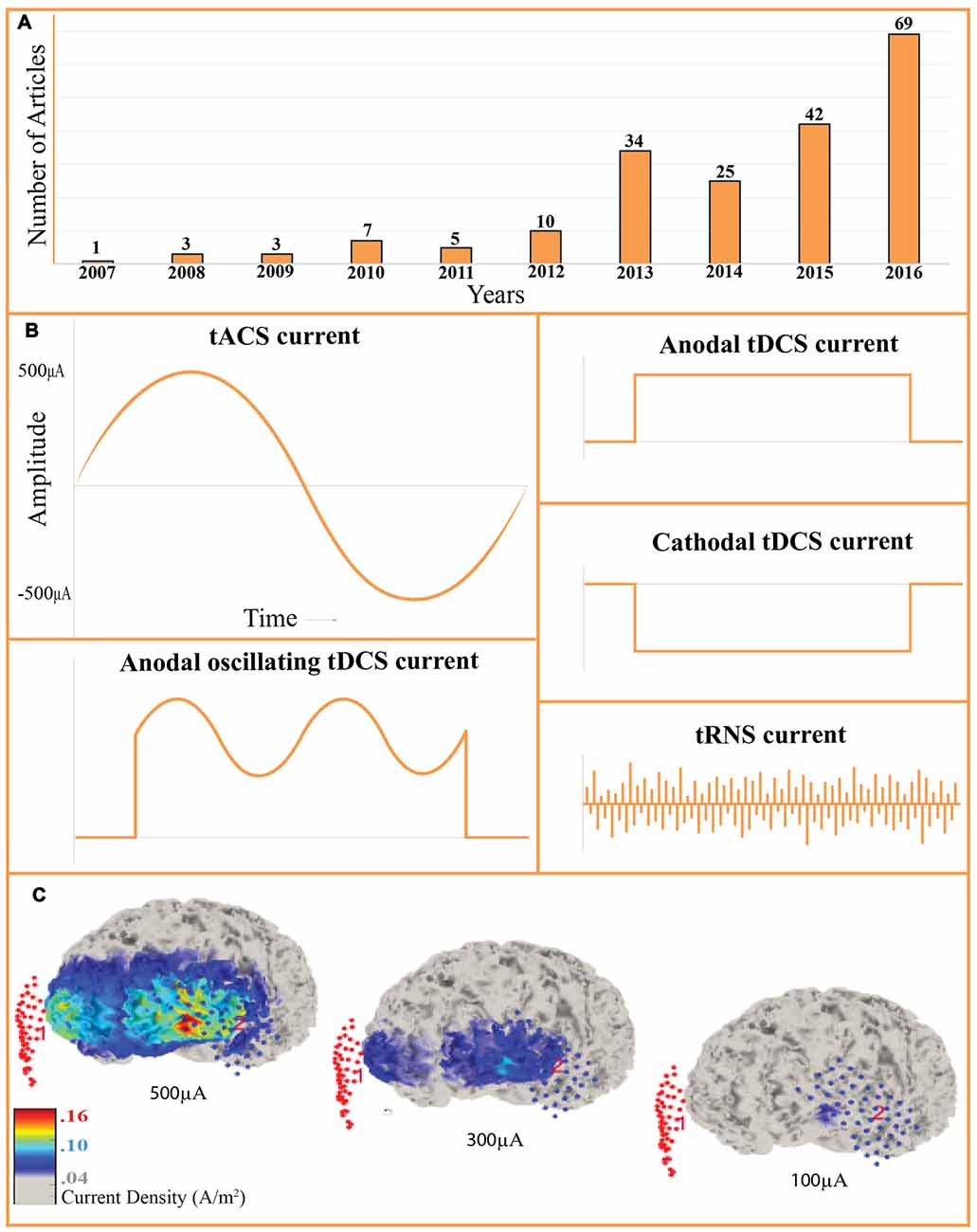
Frontiers Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) Mechanisms and Protocols
Randomized trial of transcranial alternating current stimulation for treatment of auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia, European Psychiatry

Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Modulates Risky Decision Making in a Frequency-Controlled Experiment

tACS mechanism. (A) Electrode montage shown on a 3D head model

Tom A. de Graaf's research works









