a) The diamond (native C) crystal structure (cubic, space group Fd3m;
Download scientific diagram | (a) The diamond (native C) crystal structure (cubic, space group Fd3m; a = 3.560 Å; Z = 8) features a framework of tetrahedrally coordinated carbon atoms. (b) A natural diamond crystal reflects the cubic crystal structure. The semi-translucent diamond cube (ref. no. S014632) is 24.3 × 21.8 × 21.7 mm in size and weighs 156.381 carats (31.3 gm) and is shown with a 1-carat diamond for scale. It is represented to be from Ghana. Photo courtesy of Harold and Erica Van Pelt. [Animation 2: For readers of the electronic version, click the image for an animation of the diamond crystal structure.] from publication: Carbon Mineralogy and Crystal Chemistry | INTRODUCTION Carbon, element 6, displays remarkable chemical exibility and thus is unique in the diversity of its mineralogical roles. Carbon has the ability to bond to itself and to more than 80 other elements in a variety of bonding topologies, most commonly in 2-, 3-, and | Carbon, Crystal Chemistry and Mantle | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Structural Diversity of Ordered Pyrochlores

Selected anhydrous carbonates, primarily species with more than 10

a) The diamond (native C) crystal structure (cubic, space group

Pharmaceutics, Free Full-Text

A Strategic Review on Gallium Oxide Based Deep‐Ultraviolet
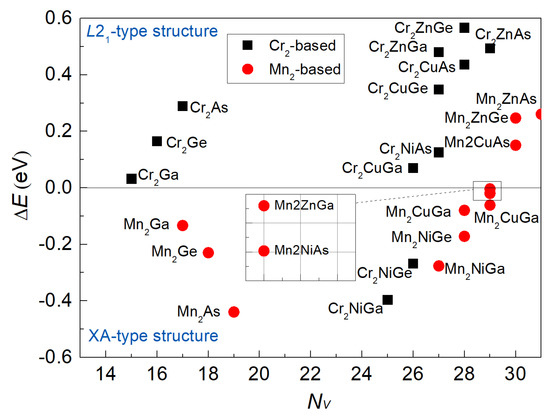
Symmetry, Free Full-Text

Scheelite structure projected on (100) with c axis vertical and b axis

Selected anhydrous carbonates, primarily species with more than 10

Style of diamond's cubic structure is in the Fd3m space group
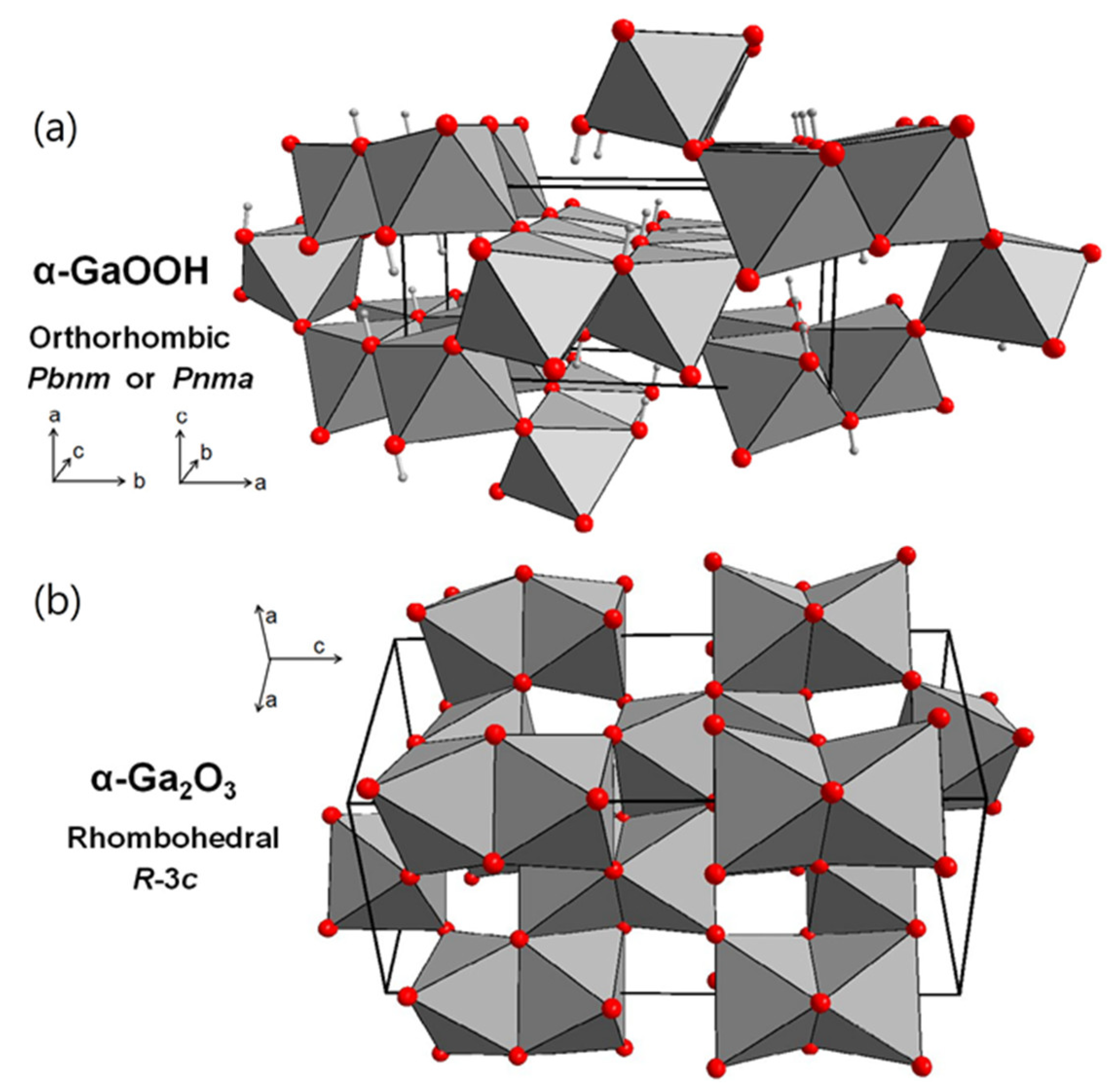
Nanomaterials, Free Full-Text

Robert HAZEN, Senior Staff Scientist, Ph.D.

Structure and Properties of Dislocations in Silicon

PDF) 2. Carbon Mineralogy and Crystal Chemistry









