Thermoplastics :: PlasticsEurope
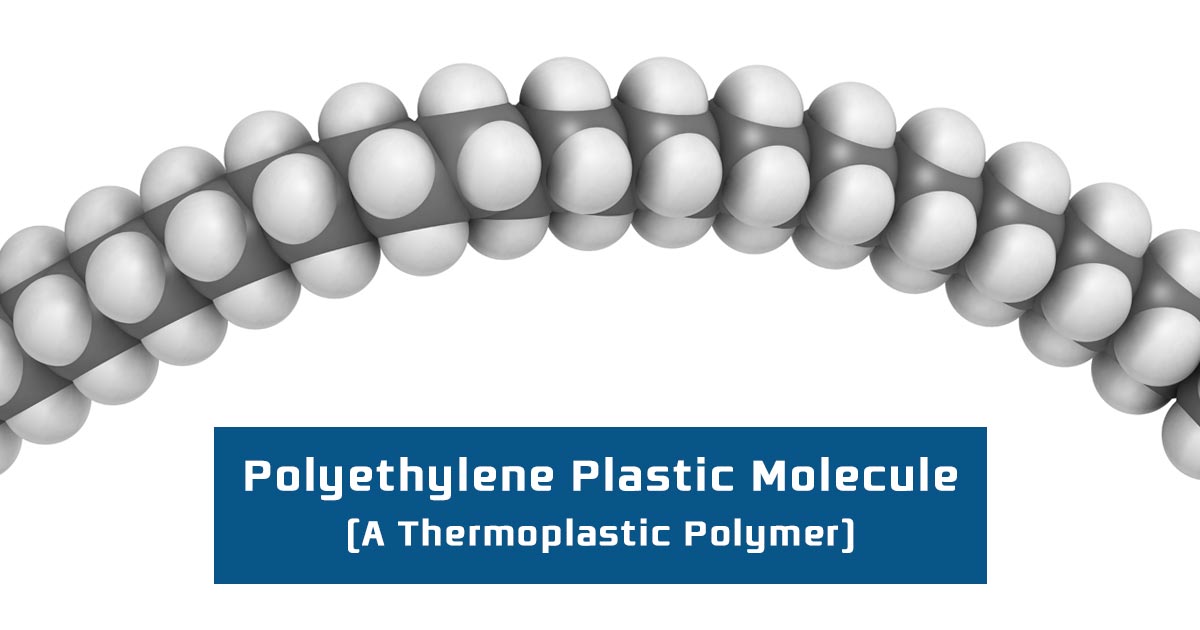
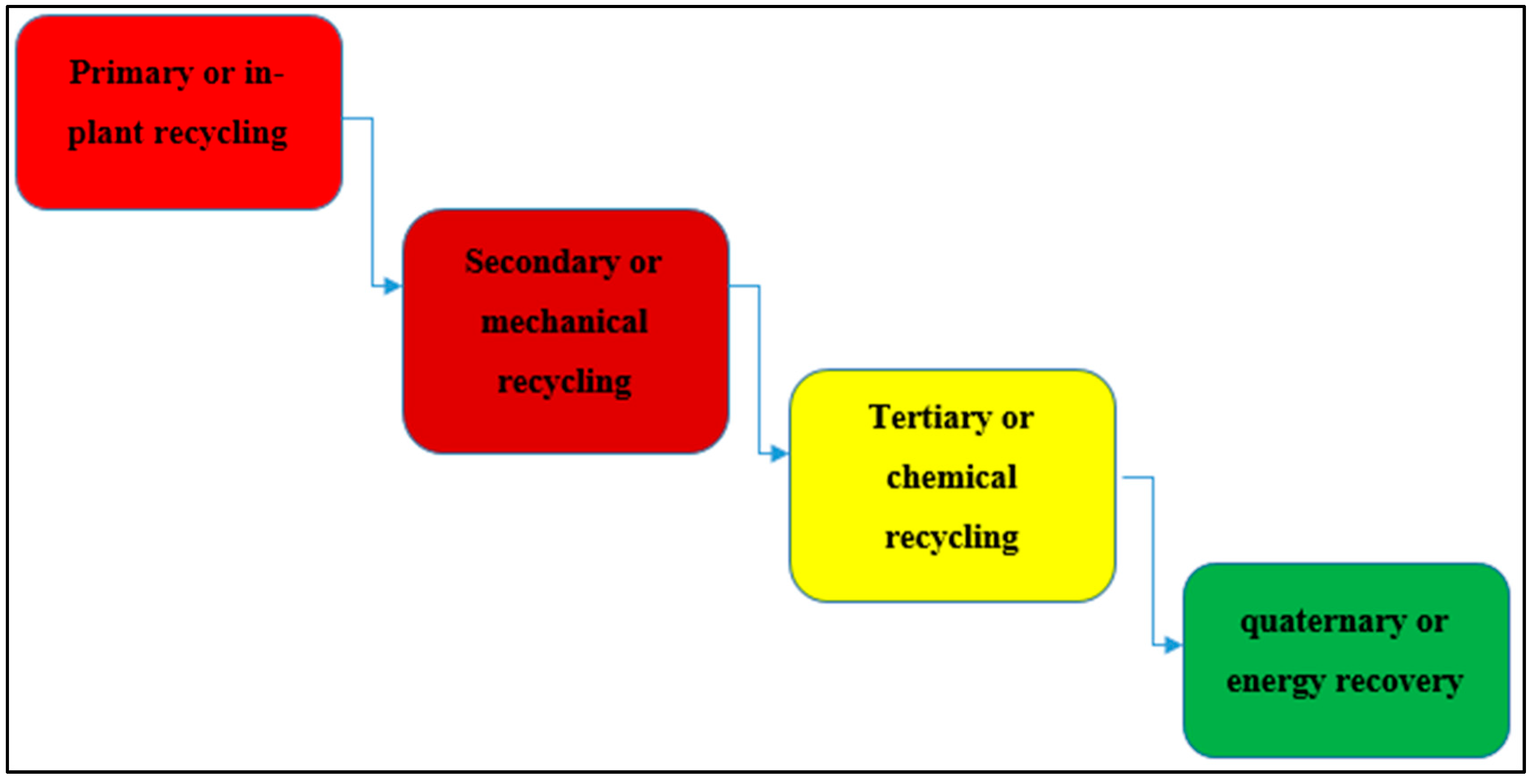
Thermoplastics are defined as polymers that can be melted and recast almost indefinitely. They are molten when heated and harden upon cooling. When frozen, however, a thermoplastic becomes glass-like and subject to fracture. These characteristics, which lend the material its name, are reversible, so the material can be reheated, reshaped, and frozen repeatedly. As a result, thermoplastics are mechanically recyclable. Some of the most common types of thermoplastic are polypropylene, polyethylene, polyvinylchloride, polystyrene, polyethylenetheraphthalate and polycarbonate.

Plastics - the facts 2014/2015 by PlasticsEurope - Issuu
J. Compos. Sci., Free Full-Text

Thermoplastics • Plastics Europe
The Global Plastics Treaty • Plastics Europe

Plastics Europe • Enabling a sustainable future
Energies, Free Full-Text

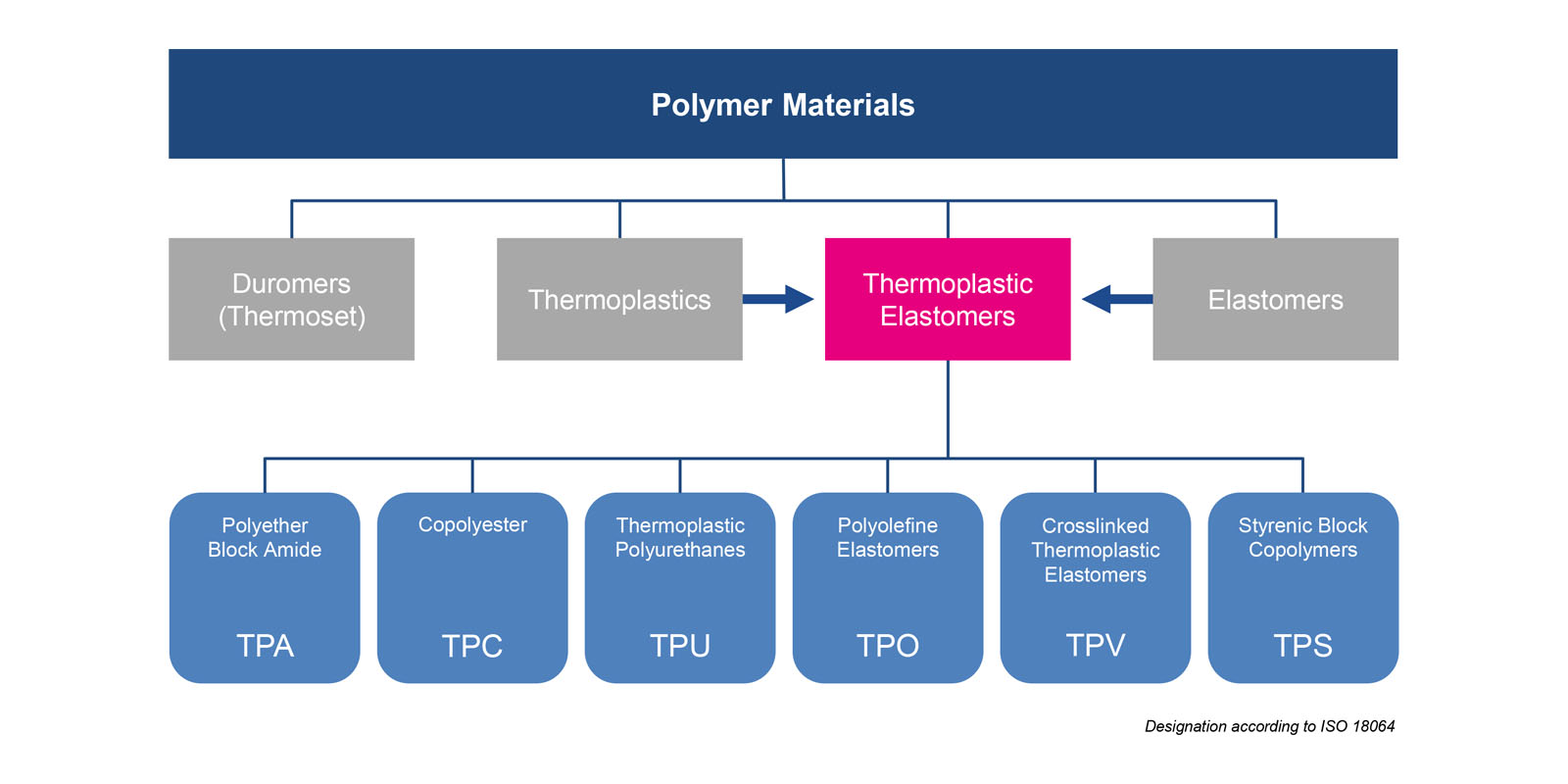
Thermosets and thermoplastics. (Adapted from PlasticsEurope 2020)

Thermoplastic composites - Tepex®

PlasticsEurope 2016 HOW PLASTICS ARE MADE. © Plastics Europe 2016 amorphous structure Standard Plastics Engineering Thermoplastics TI = °C. - ppt download

PlasticsEurope 2016 HOW PLASTICS ARE MADE. © Plastics Europe 2016 amorphous structure Standard Plastics Engineering Thermoplastics TI = °C. - ppt download

Europe: plastic production volume 1950-2021

Semicrystalline Non-Isocyanate Polyhydroxyurethanes as Thermoplastics and Thermoplastic Elastomers and Their Use in 3D Printing by Fused Filament Fabrication

Polypropylene and Other Polyolefins - ScienceDirect

PlasticsEurope 2016 HOW PLASTICS ARE MADE. © Plastics Europe 2016 amorphous structure Standard Plastics Engineering Thermoplastics TI = °C. - ppt download