Frontiers Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) Mechanisms and Protocols

Transcranial alternating current stimulation: a review of the underlying mechanisms and modulation of cognitive processes. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Neurocognitive, physiological, and biophysical effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation: Trends in Cognitive Sciences
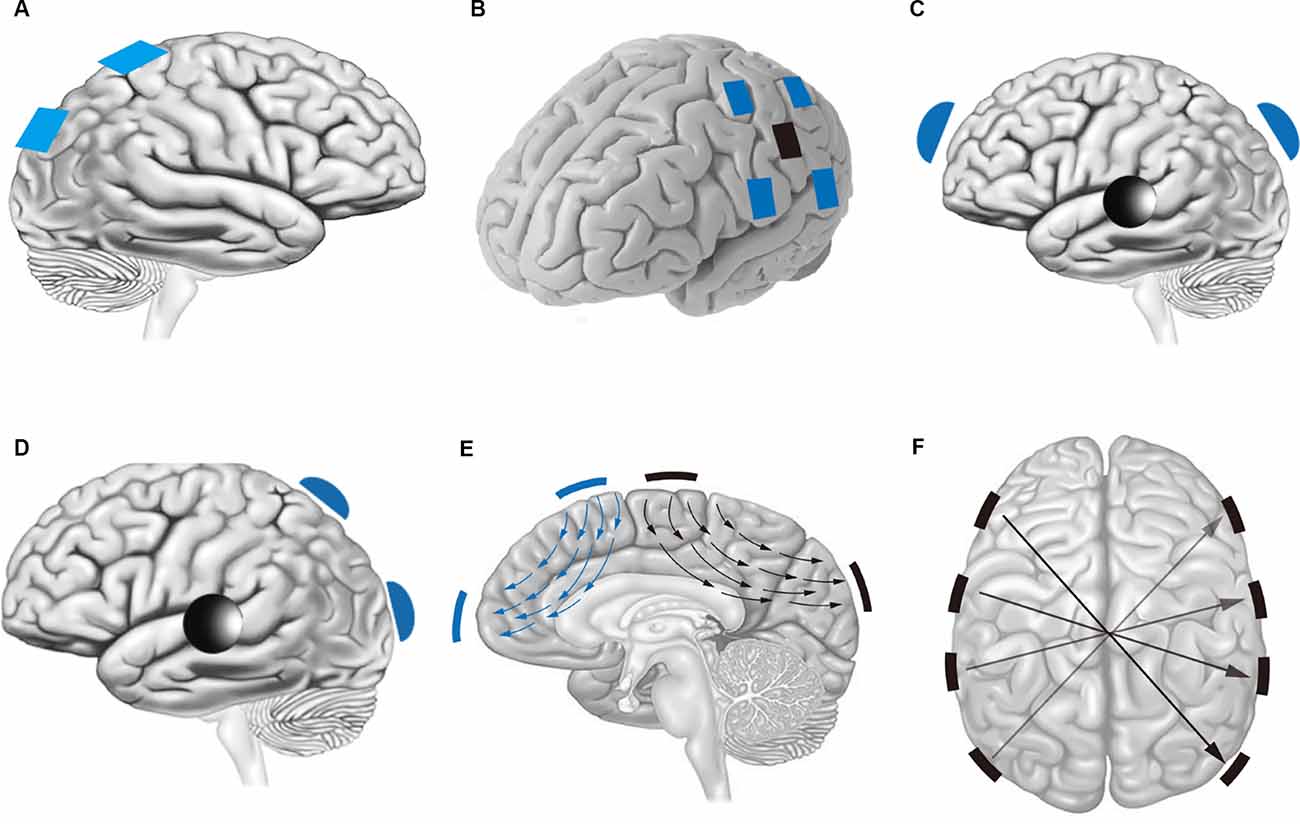
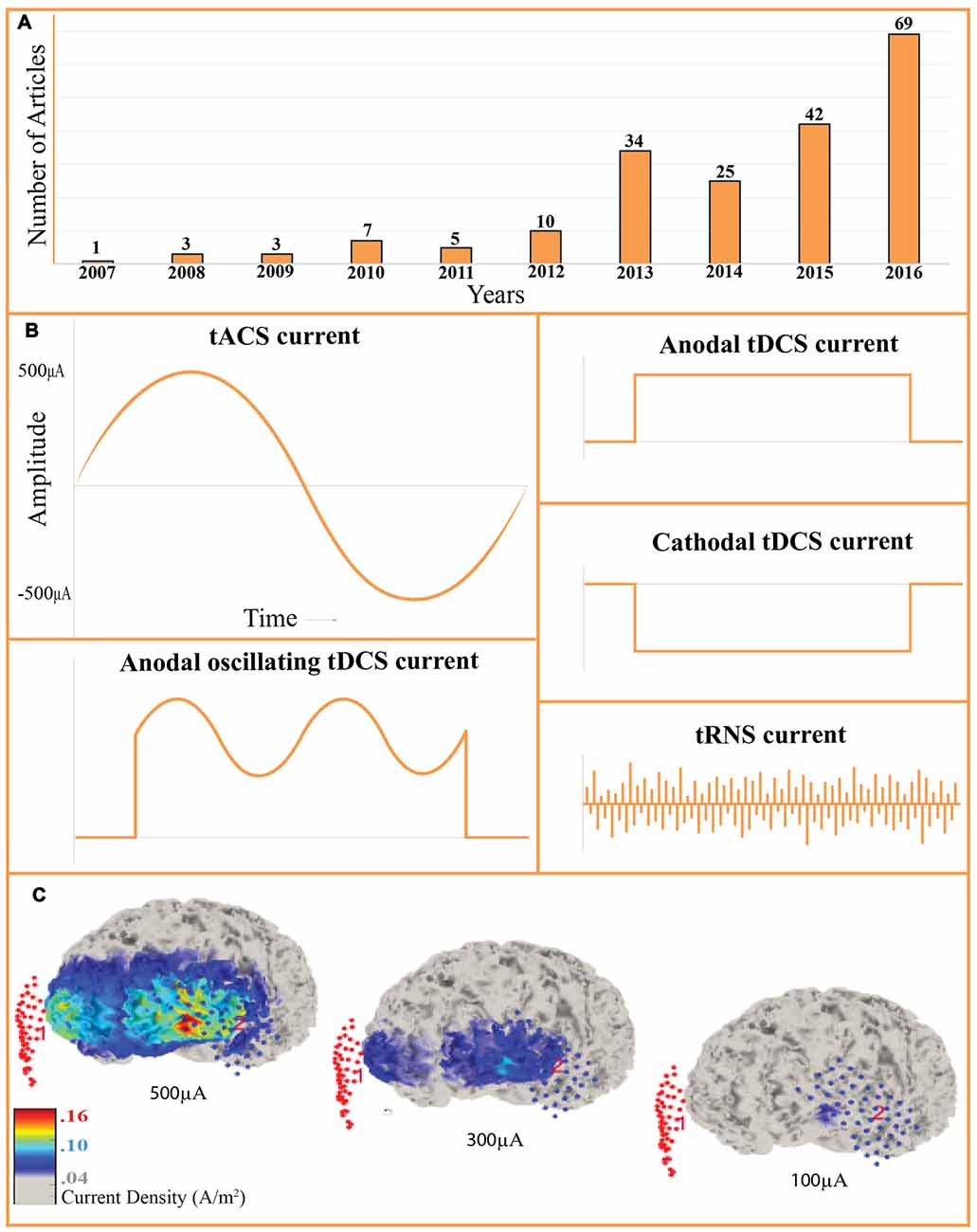
Frontiers Improving the Effect of Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS): A Systematic Review
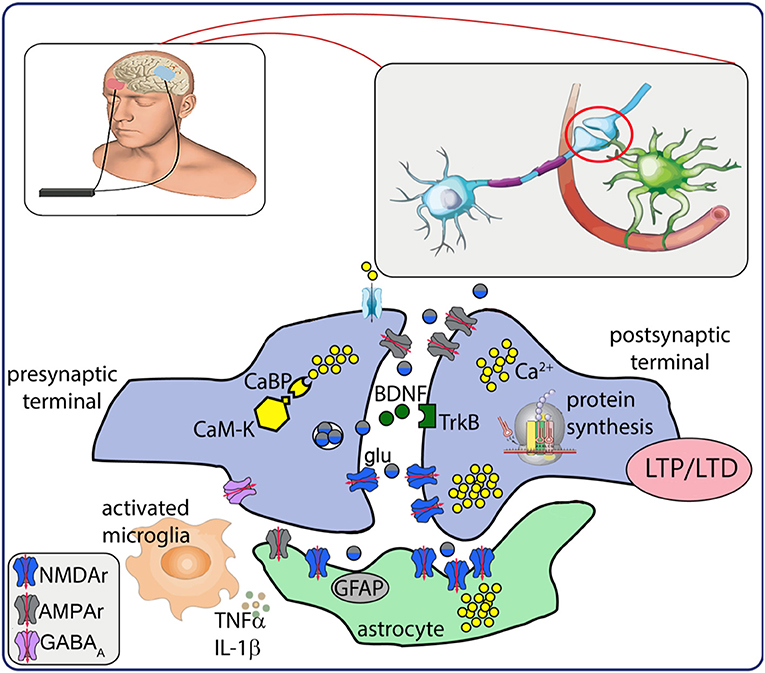
Frontiers Neurobiological After-Effects of Low Intensity Transcranial Electric Stimulation of the Human Nervous System: From Basic Mechanisms to Metaplasticity

PDF) Effects of weak transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation on brain activity – a review of known mechanisms

Phase-Synchronized Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation-Induced Neural Oscillations Modulate Cortico-Cortical Signaling Efficacy

Experimental setup for concurrent transcranial alternating current

Resumes CS TA Hiring Process After Three-day Delay The, 44% OFF

θ-γ Cross-Frequency Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation over the Trough Impairs Cognitive Control

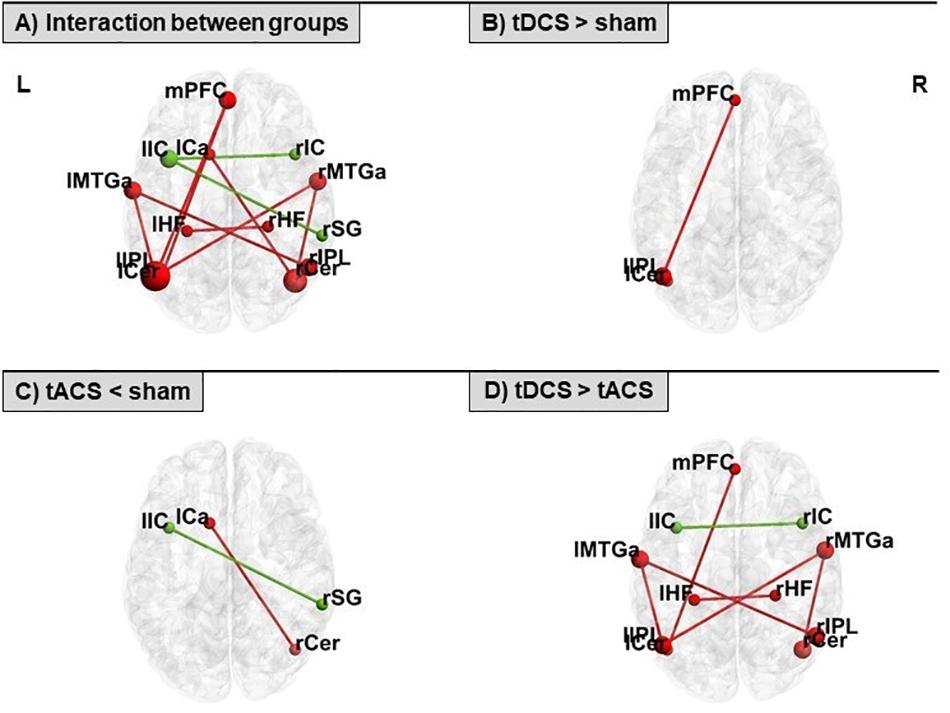
Differential tDCS and tACS Effects on Working Memory-Related Neural Activity and Resting-State Connectivity
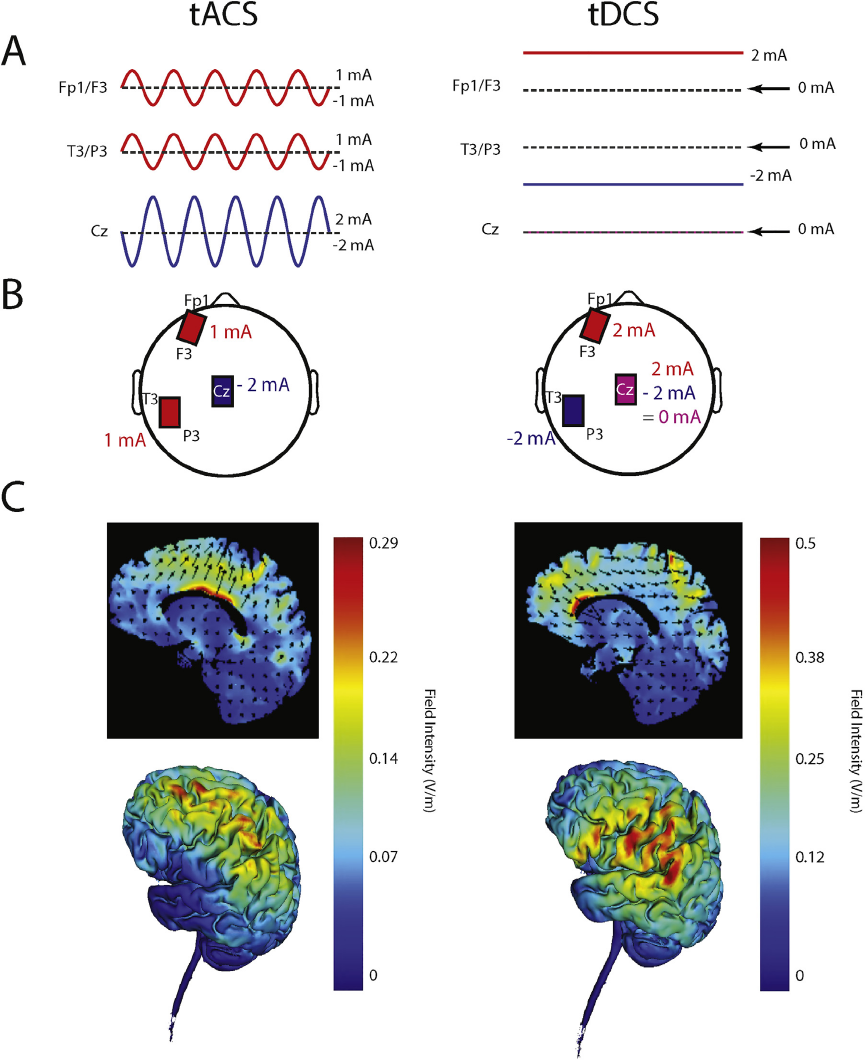
Randomized trial of transcranial alternating current stimulation for treatment of auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia, European Psychiatry

Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Modulates Risky Decision Making in a Frequency-Controlled Experiment

PDF) Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS)

Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) Explained!

Transcranial alternating current stimulation entrains single-neuron activity in the primate brain