Colour - Wavelengths, Pigments, Light
Colour - Wavelengths, Pigments, Light: According to the law of energy conservation, energy can be converted from one form to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed. Consequently, when a photon of light is absorbed by matter, usually by an atom, molecule, or ion or by a small grouping of such units, the photon disappears and its energy is gained by the matter. Similarly, when matter emits light, it loses the energy carried away by the photons. A given atom or molecule cannot emit light of any arbitrary energy, since quantum theory explains that only certain energy states are possible for a given system.
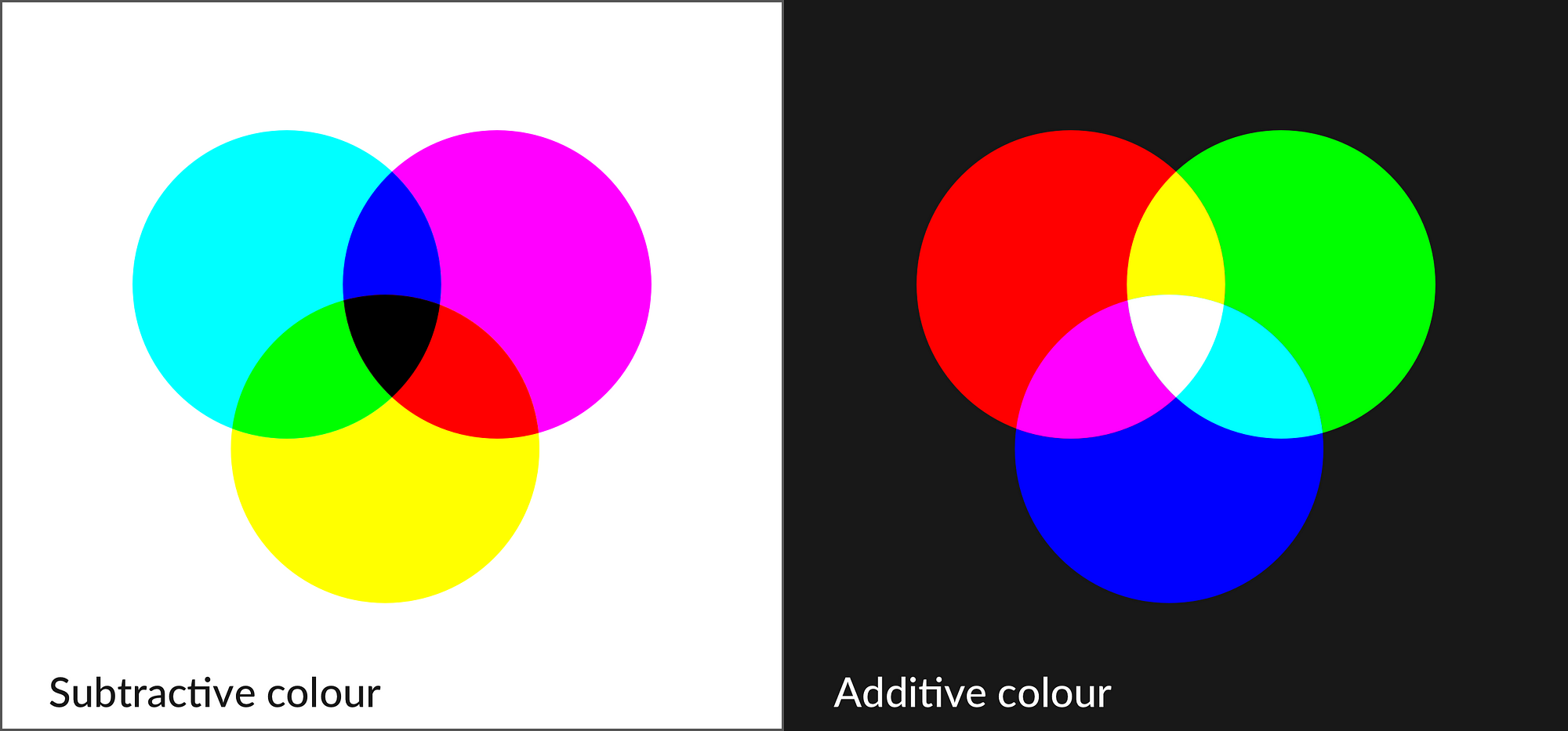
Color, the aspect of any object that may be described in terms of hue, lightness, and saturation. In physics, color is associated specifically with electromagnetic radiation of a certain range of wavelengths visible to the human eye. Learn more about color in this article.

Which wavelengths or colors are absorbed and which are transmitted by pigments in leaves of plants and the filters?
Which colour light is the best for photosynthesis between violet, blue, green, yellow, and red? - Quora

uv-visible light absorption spectra photopigments of the human eye spectrum of red cones green cones blue cones rods wavelengths of maximum absorbance Doc Brown's chemistry revision notes

Reasonably Priced RichnessWe are high vibrational beings of light

Painting with Petals Stay-at-Home Science

Colour - Wavelengths, Pigments, Light
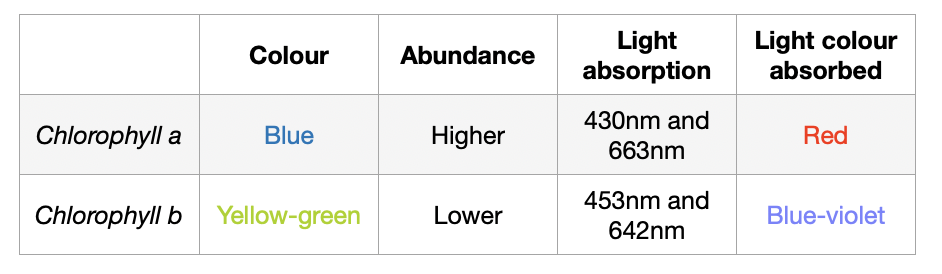
Photosystems and Photosynthetic Pigments (A-level Biology) - Study Mind
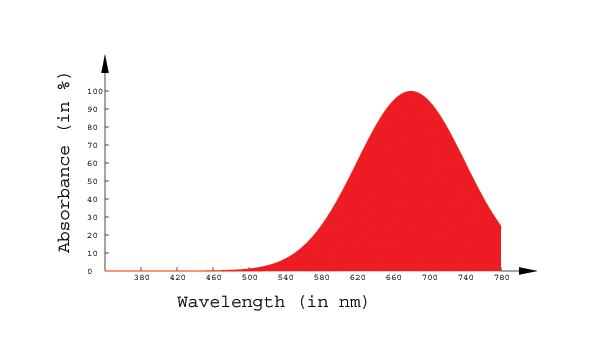
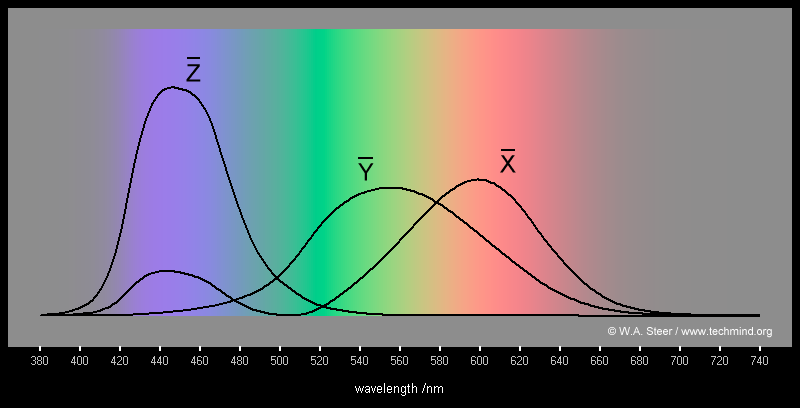
Math 309 Project: Colour Vision

Colour - Wavelengths, Pigments, Light
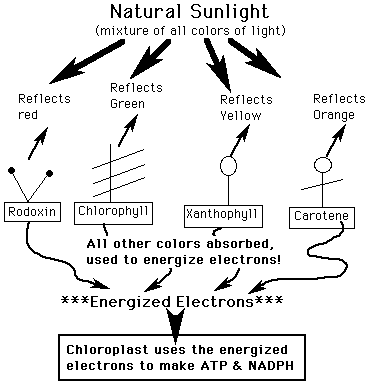
Photosynthesis: Photosynthetic Plant Pigments

Introduction to Photosynthesis